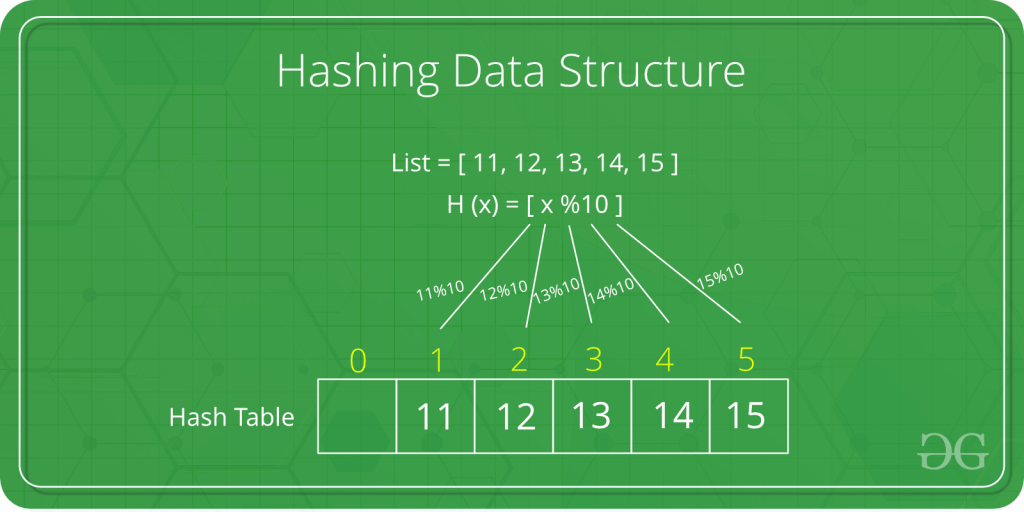
Hashing Data Structure
Introduction:
Hashing is an important Data structure which is designed to use a special function called the Hash function which is used to map a given Value with a particular key for faster access of elements.The efficiency of Mapping depends of the efficiency of the hash function used.
Index Mapping (or Trivial Hashing) with negatives allowed
Given a limited range array contains both positive and non positive numbers,i.e.,elements are in range from -MAX to +MAX. Our task is to search if some number is present in the array or not in O(1) time.
Since range is limited, we can use index mapping(or trivial hashing).We use values as index in a big array. Therefore we can search and insert elements in O(1) time.
Assign all the values of the hash matrix as 0.
Traverse the given array:
If the element ele is non negative assign
hash[ele][0] as 1.
Else take the absolute value of ele and
assign hash[ele][1] as 1.
To search any elements x in the array.
If X is non-negative check if hash[X][0] is 1 or not. If Hash[X][0] is one then the number is present else not present.
If X is negative take absolute value of X and then check if hash[X][1] is 1 or not. if hash [X][1] is one then the number is present.
Below is the implementation of the above idea.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 1000
bool has[MAX + 1][2];
bool search(int X)
{
if (X >= 0) {
if (has[X][0] == 1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
X = abs(X);
if (has[X][1] == 1)
return true;
return false;
}
void insert(int a[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] >= 0)
has[a[i]][0] = 1;
else
has[abs(a[i])][1] = 1;
}
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { -1, 9, -5, -8, -5, -2 };
int n = sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]);
insert(a, n);
int X = -5;
if (search(X) == true)
cout << "Present";
else
cout << "Not Present";
return 0;
}
Java
class GFG
{
final static int MAX = 1000;
static boolean[][] has = new boolean[MAX + 1][2];
static boolean search(int X)
{
if (X >= 0)
{
if (has[X][0] == true)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
X = Math.abs(X);
if (has[X][1] == true)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
static void insert(int a[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i] >= 0)
{
has[a[i]][0] = true;
}
else
{
has[Math.abs(a[i])][1] = true;
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a[] = {-1, 9, -5, -8, -5, -2};
int n = a.length;
insert(a, n);
int X = -5;
if (search(X) == true)
{
System.out.println("Present");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Not Present");
}
}
}
C#
// C# program to implement direct index
// mapping with negative values allowed.
using System;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 1000;
// Since array is global, it
// is initialized as 0.
static bool[,] has = new bool[MAX + 1, 2];
// searching if X is Present in
// the given array or not.
static bool search(int X)
{
if (X >= 0)
{
if (has[X, 0] == true)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// if X is negative take the
// absolute value of X.
X = Math.Abs(X);
if (has[X, 1] == true)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
static void insert(int[] a, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (a[i] >= 0)
{
has[a[i], 0] = true;
}
else
{
has[Math.Abs(a[i]), 1] = true;
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] a = {-1, 9, -5, -8, -5, -2};
int n = a.Length;
insert(a, n);
int X = -5;
if (search(X) == true)
{
Console.WriteLine(“Present”);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(“Not Present”);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by Akanksha Rai
Output:
This article is contributed by Khan Shadab Alam. If you like Learnengneeringforu
and would like to contribute, you can also write an article for our learnenrs.
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.




No comments:
Write Comments